/madparticle Command Guide
Some content on this page may have been translated by AI. The translated pages may be behind the latest version.
This chapter contains all important content related to the /madparticle command.
Incorrect command parameters may cause the client to be unable to handle a large number of particles in time, resulting in lag, or in rare cases crash the client, requiring you to uninstall the mod and remove the corresponding command block. In worse cases, your world save may become unplayable.
The /madparticle and /mp commands are theoretically almost the same, except for the following:
/madparticlewill use the default Minecraft command execution system, which means higher performance cost but no unexpected execution results./mpuses a simplified command execution process, which means lower performance cost but may produce unexpected execution results, including but not limited to crashing the game or disabling permissions for this command. Also, thewhoCanSee (entity)parameter will be ignored, i.e., forced to@a./mpprovides only limited compatibility for/execute, only supportingat [target selector], and does not support other parameters.- If other commands produce unexpected results during execution (including but not limited to (possibly silent) execution failures), please check whether the command starts with
mpor containsmp(spaces represented). If so, try to avoid using that command: MadParticle uses these two features to detect and simplify command execution. - To prevent normal players from using it arbitrarily and causing lag, the execution permission for
/madparticleand/mpis level 2.
The following are all parameters of the /madparticle command with brief descriptions. Parameter names may differ slightly from those in-game. Don't worry; you don't need to write such a long command by hand.
/madparticle /mp
// Basic Information
targetParticle (Particle) // Particle to mimic
spriteFrom (MadParticle.SpriteFrom) // Texture selection method (Random | Vary over Time)
lifeTime (int) // Duration
alwaysRender (InheritableBoolean) // Whether to ignore max particle distance (default is 32 blocks)
amount (int) // Number generated per execution
// Generation Related
px, py, pz (double) // Generation position
xDiffuse, yDiffuse, zDiffuse (double) // Position random offset
vx, vy, vz (double) // Initial velocity
vxDiffuse, vyDiffuse, vzDiffuse (double) // Velocity random offset
// Movement Related
collision (InheritableBoolean) // Whether to collide with blocks
bounceTime (int) // Max collision count
horizontalRelativeCollisionDiffuse, verticalRelativeCollisionBounce (double) // Horizontal diffusion / vertical bounce factor on collision
friction, afterCollisionFriction (float) // Friction, friction after collision
gravity, afterCollisionGravity (float) // Gravity, gravity after collision
xDeflection, zDeflection, xDeflectionAfterCollision, zDeflectionAfterCollision (float) // X, Z deflection force (before and after collision)
rollSpeed (float) // Spin speed
interactWithEntity (InheritableBoolean) // Whether to be carried by players
horizontalInteractFactor, verticalInteractFactor (double) // Horizontal interaction factor, vertical interaction factor
// Display Related
renderType (renderType) // Rendering mode
r, g, b (double > float) // Color
bloomFactor (float) // Bloom intensity, renamed to ExtraLightness
beginAlpha, endAlpha (float) // Initial / ending opacity
alphaMode (MadParticle.ChangeMode) // Opacity change mode (Linear | Exponential | Sine)
beginScale, endScale (float) // Initial / ending scale
scaleMode (MadParticle.ChangeMode) // Scale change mode (Linear | Exponential | Sine)
// Additional Content
whoCanSee (entity) // Players who can see this particle
meta (CompoundTag) // Meta command area
expireThen (madParticle command) // Generate new particle when this one expires
The following are detailed explanations of the parameters. You need to understand the meaning and value range of each parameter.
For users unfamiliar with each option, it is recommended to read each As a Reference.
- The reference values given below have not been cross-validated and may not be accurate.
- When parameters of type Vec3 (coordinates) are integers, please append
.0as needed, rather than only filling the integer part. Integers by default are CenterCorrected, meaning+0.5will be added. InheritableBooleanis a wrapper for bool, and besidesTRUEandFALSE, you can also useINHERIT. See theexpireThensection below for details.- The “undefined behavior” mentioned below generally will not cause the game to crash or severe errors; it may just cause the particle to behave unexpectedly.
targetParticle
Determines the particle you want to mimic. MadParticle (MP) will attempt to retrieve and apply the texture of the specified particle. Some particles may not be supported by MP, and no particles will be generated even if the command is entered.
spriteFrom
Determines how MP selects the texture when mimicking the particle. RANDOM means a random texture is selected; AGE means the particle's texture changes over time, like the cloud particle (white smoke when a mob dies).
lifeTime, alwaysRender, amount
lifeTime determines the duration of the particle in ticks. There is a random ±10% variance when generating particles.
Generally, you should make this value as small as possible (within the range that achieves your desired effect) to reduce the total number of particles and minimize FPS loss. If you need to create particles that last a long time, you should also combine this with controlling the amount to manage the total number of particles.
alwaysRender determines whether the particle ignores the maximum generation distance and the particle settings in game options. In vanilla MC, the maximum generation distance is 32 blocks. In Extinguish, this value has been changed to 64 blocks. For more information, see Max Particle Generation Distance.
Generally, it is recommended to keep this as FALSE; otherwise, there may be unexpected FPS loss.
amount determines the number of particles generated per command execution.
Generally, you should make this value as small as possible (within the range that achieves your desired effect) to reduce the total number of particles and minimize FPS loss. If the distance between each batch of particles generated per tick becomes too large, in addition to increasing amount, you can consider increasing Diffuse and size.
x, y, z and vx, vy, vz
x, y, z specify the position where the particle is generated. You can use ~ or ^ symbols, just like in vanilla coordinate specification.
vx, vy, vz specify the initial velocity of the particle along each axis. Generating particles at an angle might require some knowledge of trigonometry.
In a future GUI helper tool, we may add assistance for writing direction vectors.
Note: The units for vx, vy, vz are m/tick, which means the values you enter may not align with typical intuition.
x,y,zDiffuse
Determines the range within which the particle is randomly generated.
If x is 100 and xDiffuse is 5, the particle will be randomly generated in the range x = 95 ~ 105. When writing a command for the first time, it is better to set a smaller value, even 0.0, to check whether the particle's behavior meets your expectations.
vx,vy,vzDiffuse
Determines the velocity variation range when generating a particle. Note that the units are m/tick, so you generally do not need large values.
If vx is 0.2 and vxDiffuse is 0.02, the generated particles may have any value between 0.18 and 0.22 along the x-axis. If you want a firework-like effect (i.e., spreading from the center), vx=0.0, vxDiffuse=0.3 is a good starting point. When writing a command for the first time, it is better to set a smaller value, even 0.0, to check whether the particle's behavior meets your expectations.
collision, bounceTime
collision determines whether the particle will collide with blocks.
bounceTime determines the number of collisions; after exceeding this count, no further collision detection will occur.
Generally, it is recommended to keep this value below 4, unless you especially want a bouncing effect, etc.
It is worth noting that due to differences between particle textures, collisions may not appear as you expect. It is normal for particles to sink into the ground before stopping or disappear when hitting the ceiling (from a program perspective).
horizontalRelativeCollisionDiffuse, verticalRelativeCollisionBounce
horizontalRelativeCollisionDiffuse determines the horizontal dispersion range on collision.
A base value of 1 means that up to 100% of kinetic energy is used for horizontal dispersion. This will show an effect similar to a perfectly elastic collision.
verticalRelativeCollisionBounce determines the vertical bounce factor on collision.
A base value of 1 means that up to 100% of normal velocity is used for bouncing. This will show an effect similar to a perfectly elastic collision.
Here, “horizontal” and “vertical” are relative to the collision surface.
friction, afterCollisionFriction
friction determines how much the particle's speed decreases over time.
afterCollisionFriction determines the new friction value after the particle collides. If you do not need to change the friction after collision, set it equal to friction.
The friction coefficient for a player walking normally is 0.6, and on ice it is 0.98.
Friction is applied to particle velocity exponentially, i.e., each tick vx = vx * friction.
Entering a value greater than 1 is undefined behavior.
gravity, afterCollisionGravity
gravity determines the magnitude of gravity acting on the particle during its movement.
afterCollisionGravity determines the new gravity value after the particle collides. If you do not need to change gravity after collision, set it equal to gravity.
A gravity value of 0.01 can show a slow falling effect, 0.02-0.03 is closer to a normal falling effect, and higher values show a heavy object falling quickly (Aristotle would be thrilled).
Unlike friction, gravity acts linearly at 0.04 times the particle's velocity.
xDeflection, zDeflection, xDeflectionAfterCollision, zDeflectionAfterCollision
xDeflection, zDeflection determine the deflection force acting on the particle during movement, similar to horizontal gravity, acting linearly.
xDeflectionAfterCollision, zDeflectionAfterCollision determine the deflection force on the particle after a collision.
rollSpeed
rollSpeed determines the particle's spin speed, like lifeTime, with ±10% random variance. Non-zero values will cause the particle to have a random initial rotation when generated.
A value of 1 means rotating 360° per tick.
If you want a particle to have a random initial rotation but no subsequent rotation, you can set this value to a very small non-zero number.
interactWithEntity, horizontalInteractFactor, verticalInteractFactor
interactWithEntity determines whether the particle will be carried by players when they pass by.
horizontalInteractFactor determines how much horizontal velocity the particle can gain when disturbed. A base value of 1 means it can gain up to the same horizontal velocity as the player.
verticalInteractFactor determines how much vertical velocity the particle can gain when disturbed. When calculating, take the larger of the player's vertical velocity and the geometric mean of the player's horizontal velocities, then multiply by this factor.
In Extinguish, the dry powder particle interaction factors are 0.3 and 0.12 respectively.
Due to discrepancies between client and server data, the disturbance effect generated by the local client player often differs in strength compared to that generated by other players.
renderType
Determines the particle's rendering mode.
If you are not familiar with this option, there are three recommended choices:
INSTANCED: Very high rendering efficiency, does not support Shimmer-linked bloom, does not support shaders, allows particles to have semi-transparency;PARTICLE_SHEET_TRANSLUCENT: Supports Shimmer-linked bloom, will automatically downgrade to vanilla no-bloom when using shaders, allows particles to have semi-transparency;PARTICLE_SHEET_OPAQUE: Supports Shimmer-linked bloom, will automatically downgrade to vanilla no-bloom when using shaders, does not allow particles to be semi-transparent;
The latter two have some special modifications to allow a wider range of color settings in certain cases (see below). We have made changes targeting common rendering/optimization mods, but compatibility issues may still exist; if you encounter issues, please provide feedback promptly.
Without understanding, do not choose CUSTOM.
r, g, b
Determines how the particle's texture color will change. Values less than 0 are treated as 0, with no hard upper limit.
(1,1,1) renders the texture using its original color.
(3,1,1) triples the red component of the texture while keeping the other color channels unchanged. Note that the final result is usually clamped to 255. For example, (123,123,123) × (3,1,0.4) = (255,123,49).
bloomFactor ExtraLightness
In MadParticle 0.8.0+, the meaning of this entry has changed and it is no longer a Shimmer linkage item.
Determines the particle's extra brightness multiplier. Allows additional brightness beyond vanilla's 0~15 light levels.
When not using a shader pack, increasing the particle brightness will show a clear saturation limit without other effects; when using a shader pack, this option can be compatible with the shader pack's Bloom option, making the particle appear brighter visually. The effect on HDR is currently unclear.
Range is 1~255. 1 means using only vanilla brightness; other values represent brightness multipliers.
Different clients may render visually differently depending on the shader pack used or parameter settings.
beginAlpha, endAlpha, alphaMode
beginAlpha determines the particle's opacity when generated.
endAlpha determines the particle's opacity when it disappears. If no opacity change is needed, set it equal to beginAlpha. Range is 0-1 for both.
alphaMode determines how the particle's opacity changes. linear means linear change, index means exponential change, sin means sine change. If no opacity change is needed, set alphaMode to linear.
1 means fully opaque; 0 means fully transparent.
Assuming beginAlpha is 1 and endAlpha is 0.1 (a particle that gradually fades), and the particle's lifetime is 100 ticks (5 seconds), the three change mode curves are simulated as shown:
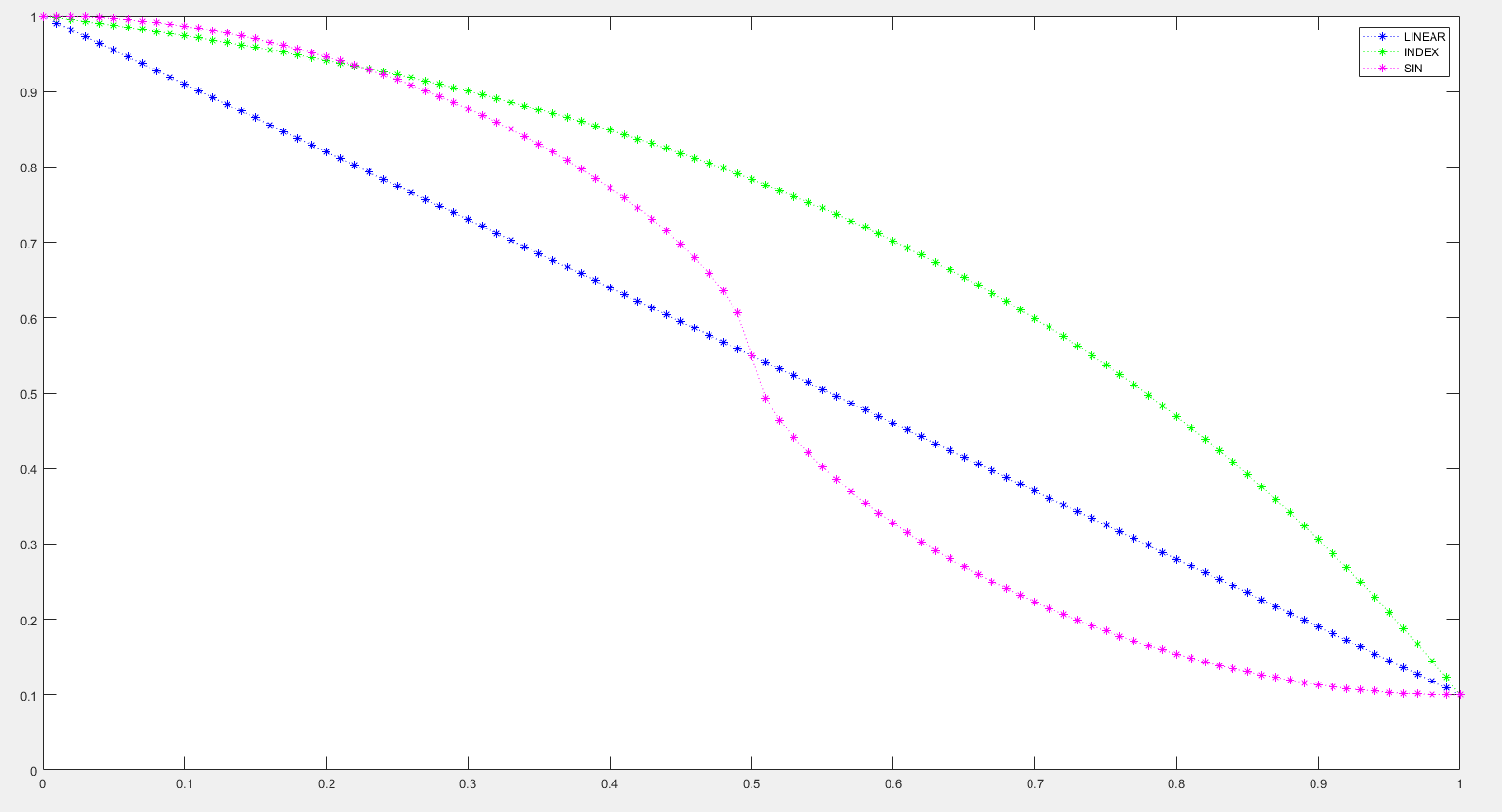
In order to better highlight the difference from other methods, the base for exponential changes is set to 10.
Sine changes use the sin function raised to the power of 3/5 to emphasize the difference from linear, and to simplify computations, lookup tables and linear interpolation are used.
beginScale, endScale, scaleMode
beginScale determines the particle's scale when generated.
endScale determines the particle's scale when it disappears. If no size change is needed, set it equal to beginScale.
scaleMode determines how the particle's scale changes. The three options are the same as the opacity change modes above.
As a reference, 1 means the particle is at its original size. Larger values make the particle bigger.
Assuming beginScale is 0.3 and endScale is 4.5 (a particle that keeps growing), and the particle's lifetime is 100 ticks (5 seconds), the three change mode curves are simulated as shown:
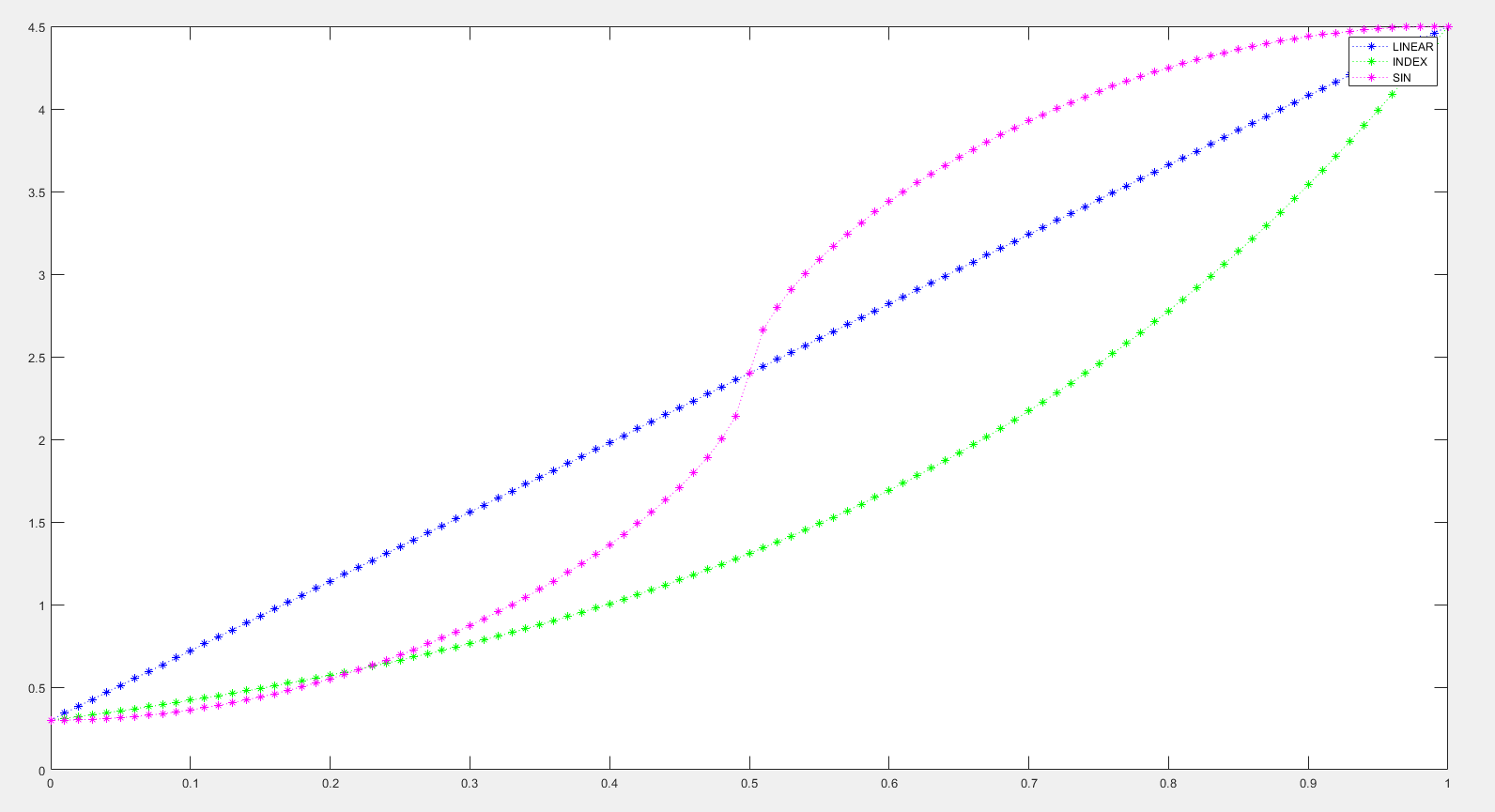
The following content is optional and not required.
whoCanSee
Thanks to
@MalayPfor the suggestion.
whoCanSee determines which players will receive the particle data. Like vanilla commands, it uses an entity target selector. If not specified, the particle is sent to all players in the same dimension by default.
meta
This is a meta command area presented as a CompoundTag. You can fill in the key-value pairs as needed.
Refer to the Meta Command Parameter Guide page to learn about all available features.
expireThen
Thanks to
@MalayPfor the suggestion.
expireThen determines what particle will be generated when the current particle expires. It must follow a specified whoCanSee and be followed by a full madparticle command. This means one entire mp command can extend in a nested fashion, where a parent particle can have a chain of child particles.
- The maximum character length allowed in the chat window is 256, which means it does not support nested commands; command blocks allow a maximum length of 32,500, so in theory you can nest about 161 (i.e., 162 total, assuming 200 characters per command) child particle commands. However, overly complex nesting may lead to huge network packets, excessive memory usage, and other potential issues.
- Unlike the first
mpcommand that spawns the parent particle, in child particle commands you can fill=(for numeric parameters) orINHERIT(for boolean (represented by enum) and enum parameters), which indicates that the child particle inherits that parameter from its parent particle. =is similar to~or^, but the difference is that=has a simple highest priority; its presence will override all other numbers for that parameter. Therefore, not only can=indicate “inherit this parameter from the parent particle,” but=-1=,3=,==1==2==3==are also accepted and mean the same. Of course, this is not recommended.- Do not use
=orINHERITin the parameters of the top-level parent particle (even if not highlighted in red), as this may lead to unexpected behavior. - The
amountparameter of child particles will be ignored and remain as 1. We recommend that you also input 1, rather than other values (although it won’t cause issues). - The
whoCanSeeparameter of the parent particle will be ignored, with the lastwhoCanSee(i.e., that of the deepest child particle) taking precedence.
The following parameters with
✅can be inherited, allowing=orINHERIT;❌cannot be inherited, and you must explicitly specify a value;🔘means the value will be ignored.... expireThen
// Basic Information
❌ targetParticle (Particle) // Particle to mimic
✅ spriteFrom (MadParticle.SpriteFrom) // Texture selection method (Random | Vary over Time)
✅ lifeTime (int) // Duration
✅ alwaysRender (InheritableBoolean) // Whether to ignore max particle distance (default is 32 blocks)
🔘 amount (int) // Number generated per execution <Ignored to prevent exponential growth in child particles>
// Generation Related
✅ px, py, pz (double) // Generation position
❌ xDiffuse, yDiffuse, zDiffuse (double) // Position random offset
✅ vx, vy, vz (double) // Initial velocity
❌ vxDiffuse, vyDiffuse, vzDiffuse (double) // Velocity random offset
// Movement Related
✅ collision (InheritableBoolean) // Whether to collide with blocks
✅ bounceTime (int) // Max collision count
✅ horizontalRelativeCollisionDiffuse, verticalRelativeCollisionBounce (double) // Horizontal diffusion / vertical bounce factor on collision
❌ friction, afterCollisionFriction (float) // Friction, friction after collision <Ambiguous, not allowed to inherit>
❌ gravity, afterCollisionGravity (float) // Gravity, gravity after collision <Ambiguous, not allowed to inherit>
❌ xDeflection, zDeflection, xDeflectionAfterCollision, zDeflectionAfterCollision (float) // X, Z deflection force <Ambiguous, not allowed to inherit>
✅ rollSpeed (float) // Spin speed
✅ interactWithEntity (InheritableBoolean) // Whether to be carried by players
✅ horizontalInteractFactor, verticalInteractFactor (double) // Horizontal interaction factor, vertical interaction factor
// Display Related
❌ renderType (renderType) // Rendering mode
✅ r, g, b (double > float) // Color
✅ bloomFactor (float) // Bloom intensity
❌ beginAlpha, endAlpha (float) // Initial / ending opacity <Ambiguous, not allowed to inherit>
✅ alphaMode (MadParticle.ChangeMode) // Opacity change mode (Linear | Exponential | Sine)
❌ beginScale, endScale (float) // Initial / ending scale <Ambiguous, not allowed to inherit>
✅ scaleMode (MadParticle.ChangeMode) // Scale change mode (Linear | Exponential | Sine)
// Additional Content
🔘 whoCanSee (entity) // Players who can see this particle <Not available for child particles>
❌ meta
expireThen ...